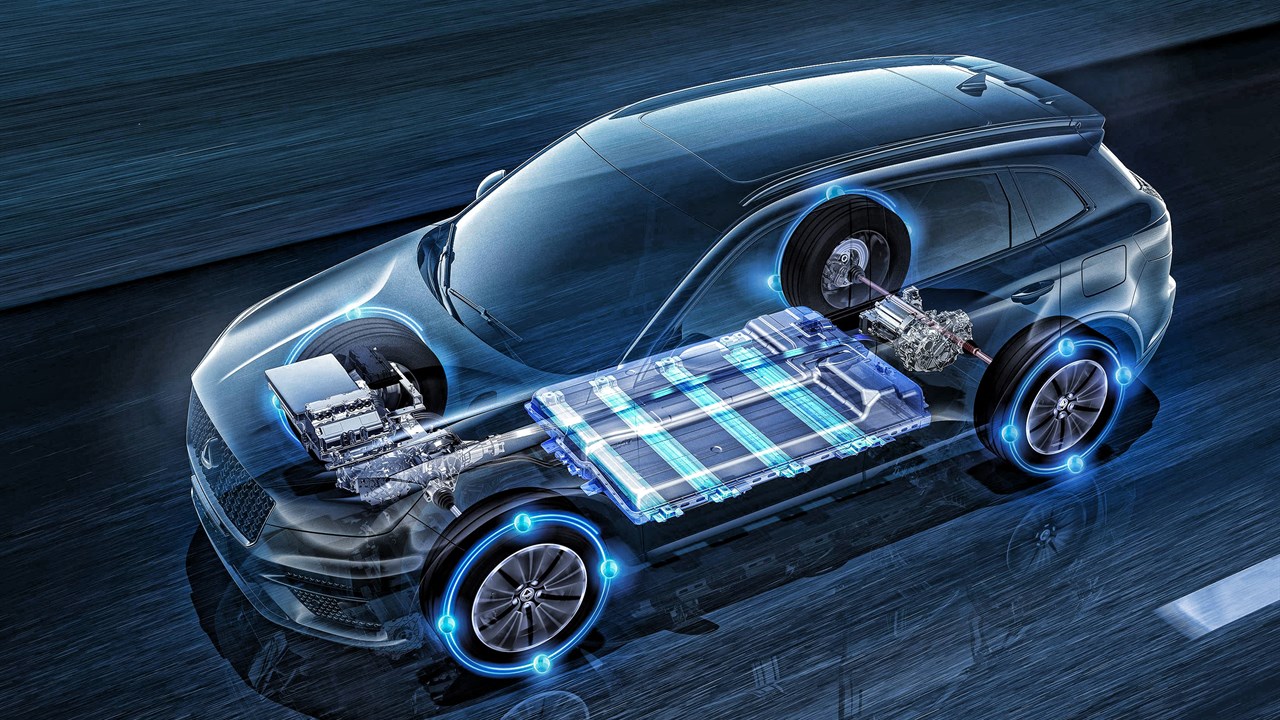
Electric Vehicle (EV) batteries are the backbone of electrification. The right chemistry balances energy density, safety, cost, lifespan, and environmental impact. Today, automakers use a mix of proven lithium-ion variants and emerging next-generation technologies to meet different needs.
AI Quick Summary
API error: models/gemini-1.5-pro-latest is not found for API version v1beta, or is not supported for generateContent. Call ListModels to see the list of available models and their supported methods.
This summary was generated by AI using this article’s content.
Read Next
What Are the Main Types of EV Batteries?
The most common EV battery chemistries include:
- Lithium-Ion (LFP, NMC, NCA variants)
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH)
- Lead-Acid
- Solid-State
- Sodium-Ion
How Do Lithium-Ion Variants Differ From Each Other?
What Is Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)?
- Chemistry: LiFePO₄ cathode with carbon anode.
- Energy Density: 150–205 Wh/kg.
- Strengths: Excellent safety, long cycle life (2,000+), cobalt-free.
- Weaknesses: Lower voltage and limited driving range.
- Use Cases: Entry-level EVs, two-wheelers, taxis, and storage.
What Are Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) and Nickel Cobalt Aluminium (NCA)?
- Chemistry: Nickel-rich layered oxides.
- Energy Density: 250–300+ Wh/kg.
- Strengths: High range, compact design.
- Weaknesses: Expensive, cobalt supply risk, needs strong cooling and BMS.
- Use Cases: Premium EVs like Tesla, Mercedes, and Hyundai.
Are Next-Generation Batteries Ready for EVs?
What Are Solid-State Batteries?
- Electrolyte: Solid ceramics, sulfides, or polymers.
- Energy Density: 350–500 Wh/kg (lab).
- Benefits: Ultra-safe, 8,000–10,000 cycles, fast charging (10–80% in ~10 min).
- Challenges: Very costly, difficult to scale up.
- Status: Pilot production, mass-market expected in the late 2020s.
What Are Sodium-Ion Batteries?
- Chemistry: Sodium ions between the carbon anode and the oxide/polyanion cathode.
- Energy Density: ~200 Wh/kg (CATL’s 2025 cells).
- Benefits: Low cost, abundant sodium, strong at extreme temperatures.
- Limitations: Heavier and lower specific energy than lithium.
- Status: Early commercial use in low-cost EVs and storage systems.
Do Older Battery Types Still Play a Role?
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH): Mostly hybrids, reliable but low energy density.
- Lead-Acid: Phased out, used today only as auxiliary 12V batteries.
- Nickel-Cadmium: Rare in EVs due to toxicity and low efficiency.
How Do Different EV Batteries Compare?
| Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cost Profile | Cycle Life | Safety | Commercial Maturity |
| LFP | 150–205 | Low | 2,000+ | Excellent | High |
| NMC / NCA | 250–300+ | High | 1,000–2,000 | Moderate | Very High |
| Solid-State | 350–500 (lab) | Very High | 8,000–10,000 | Superior | Pilot |
| Sodium-Ion | ~200 | Very Low | 20,000 | Good | Early Commercial |
Which EV Battery Is Right for You?
- Budget & City Driving: LFP is cost-effective, safe, and long-lasting.
- Long-Range & Premium Cars: NMC/NCA deliver more range per kg.
- Future Flagship Models: Solid-State promises ultra-fast charging and maximum safety.
- Eco-Friendly Mass Market: Sodium-Ion is emerging as a sustainable alternative.
What Does the Future Hold for EV Batteries?
Battery innovation is moving fast. Solid-state and sodium-ion technologies may change the industry by improving safety, reducing reliance on rare materials, and cutting costs. For now, lithium-ion remains the foundation of EV technology worldwide.
Find the best electric cars for sale in the UAE.
Stay tuned to UAE’s most popular auto blog for more information about the latest happenings in all of the Emirates.
FAQs
What are the main types of EV batteries?
The main EV battery types are Lithium-Ion (LFP, NMC, NCA), Solid-State, Sodium-Ion, Nickel-Metal Hydride, and Lead-Acid. Lithium-Ion dominates today, while Solid-State and Sodium-Ion are emerging technologies.
Which battery is best for electric cars?
Lithium-Ion batteries, especially NMC and NCA, are the best today for long range and performance. LFP is best for budget EVs, while Solid-State may become the best option in the future.
How long do EV batteries last?
Most EV batteries last 8–15 years, depending on chemistry and usage. LFP batteries can exceed 2,000 cycles, while Solid-State promises 8,000–10,000 cycles once commercialised.
Are solid-state batteries better than lithium-ion?
Yes, in theory. Solid-State offers higher energy density, faster charging, and better safety than lithium-ion. However, they are still expensive and not yet widely available in mass-market EVs.
What is the future of EV batteries?
The future includes Solid-State for premium performance and Sodium-Ion for affordable, sustainable options. Advances in materials and manufacturing will continue to lower costs and extend lifespan across all EV battery types.
Electric Vehicle (EV) batteries are the backbone of electrification. The right chemistry balances energy density, safety, cost, lifespan, and environmental impact. Today, automakers use a mix of proven lithium-ion variants and emerging next-generation technologies to meet different needs. What Are